Loading... # 查看进程 ```shell ps -aux ``` ## 序列解释: | USER | PID | %CPU | %MEM | VSZ | RSS | TTY | STAT | START | TIME | COMMAND | | ------ | -------- | ----------- | ------------ | ------------------ | ---------------------- | -------- | ---------- | ---------- | ---------- | ------------ | | 用户 | 进程ID | cpu使用率 | 内存使用率 | 虚拟内存占用大小 | 实际物理内存使用大小 | 终端号 | 进程状态 | 启动时间 | 执行时间 | 运行命令行 | ### 进程状态解释 具体解释可参阅`man ps` PROCESS STATE CODES Here are the different values that the s, stat and state output specifiers (header "STAT" or "S") will display to describe the state of a process: ```bash D uninterruptible sleep (usually IO) I Idle kernel thread 空闲内核线程 R running or runnable (on run queue) 运行状态 S interruptible sleep (waiting for an event to complete) 休眠状态 T stopped by job control signal 暂停 t stopped by debugger during the tracing 暂停 W paging (not valid since the 2.6.xx kernel) X dead (should never be seen) 死亡进程 Z defunct ("zombie") process, terminated but not reaped by its parent 僵尸进程 For BSD formats and when the stat keyword is used, additional characters may be displayed: < high-priority (not nice to other users) 高优先级 N low-priority (nice to other users) 低优先级 L has pages locked into memory (for real-time and custom IO) s is a session leader 领导者,其下有子进程 l is multi-threaded (using CLONE_THREAD, like NPTL pthreads do) + is in the foreground process group ``` # 进程操作 python demo ```python import time for i in range(0,9999): print(i) time.sleep(1) ``` 执行`ps -aux | grep python`  此时可以看到python3 test.py进程是`S+` 执行`kill -STOP 490142`,再次执行`ps -aux | grep python` 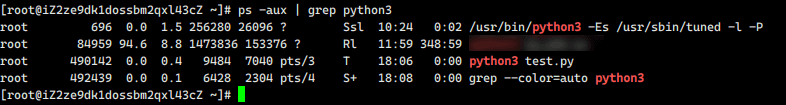 此时可以看到python3 test.py进程是`T` 而运行的python的标签显示 `[1]+ Stopped python3 test.py ` 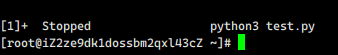 执行`fg`可继续运行进程 `fg`**将后台运行的或挂起的任务(或作业)切换到前台运行**  也可以使用`kill -CONT 490142`继续运行,但是这种运行会恢复控制台的输入,相当于后台运行  # 用途 比如说某个进程一致存在写库操作,但是发现数据库可能存在一些问题,但是又不方便关闭这个程序,需要验证是否存在问题时,可暂停这个进程,检查完之后在做决定。 © 允许规范转载 打赏 赞赏作者 支付宝微信 赞 如果觉得我的文章对你有用,请随意赞赏